| 03 |
|
 |
 |
Density functional theory (DFT) is among the most popular and versatile methods available in condensed-matter physics, computational physics, and computational chemistry. DFT is a quantum mechanical modeling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure (principally the ground state) of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. With this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by using functionals, i.e. functions of another function, which in this case is the spatially dependent electron density. Hence the name density functional theory comes from the use of functionals of the electron density. |
|
|
|
 |
|
Within DFT mapped exactly, without introducing empirical parameters, onto an effective single particle problem. The single particle problem can then be solved very efficiently using highly parallelized computer codes and thus allows the accurate ab initio calculation of a large variety of materials properties. The huge impact of DFT on today's understanding of materials properties was recognized by the Nobel Prize in chemistry for Walter Kohn in 1998. |
|
|
|
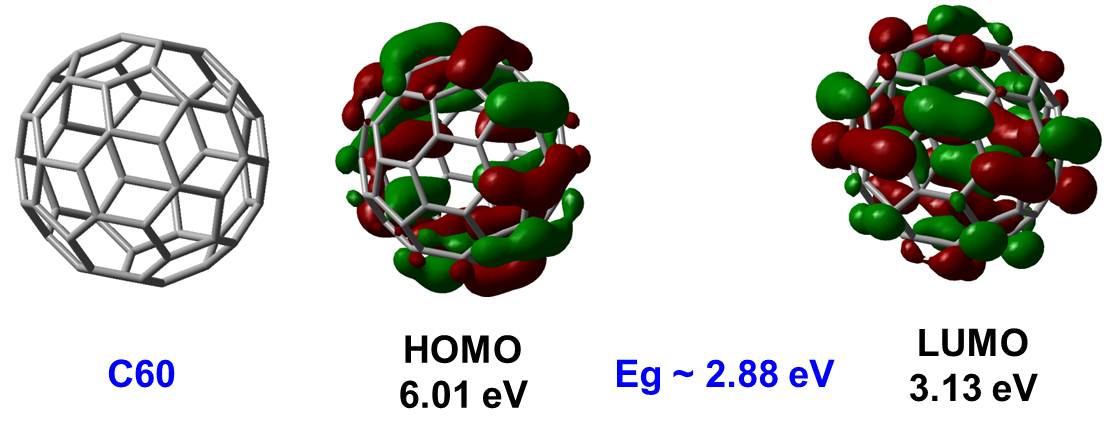
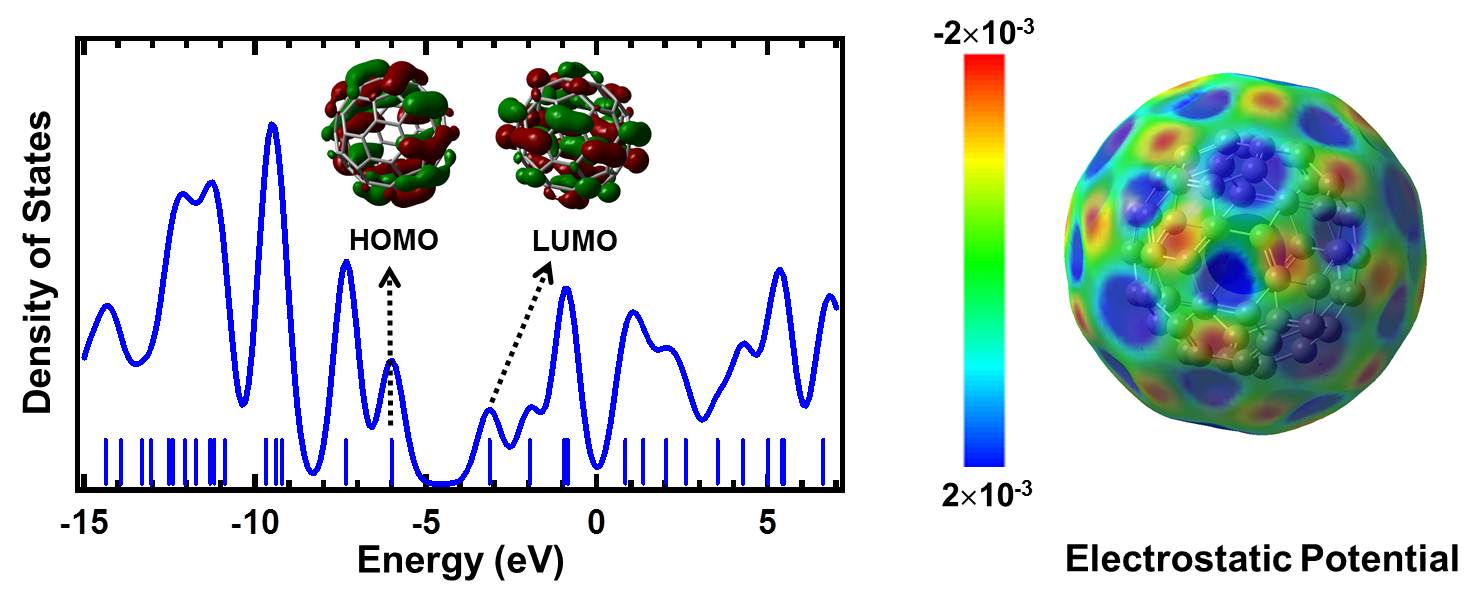
| Figures show the DFT results of a small molecule C60. The calculation was performed with B3LYP/6-31G basis using Gaussian 03 software. | |
| References | |
1. Seo, J. H.; Kim, C. Y.; Kang, S. J.; Yoo, K. -H.; Whang, C. N.; Moewes, A.; Chang, G. S. J. Chem.Phys. 2007, 126, 064706. 2. Cho, S.; Seo, J. H.; Kim, S. H.; Song, S.; Jin, Y. ; Lee, K.; Suh, H.; Heeger, A. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 263301. 3. Cho, S. W.; Yi, Y.; Seo, J. H.; Kim, C. Y.; Noh, M.; Yoo, K.-H.; Jeong, K.; Whang, C.-N.Synth.Metals, 2007, 157, 160. 4. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Density_functional_theory |
|