| 03 |
|
 |
 |
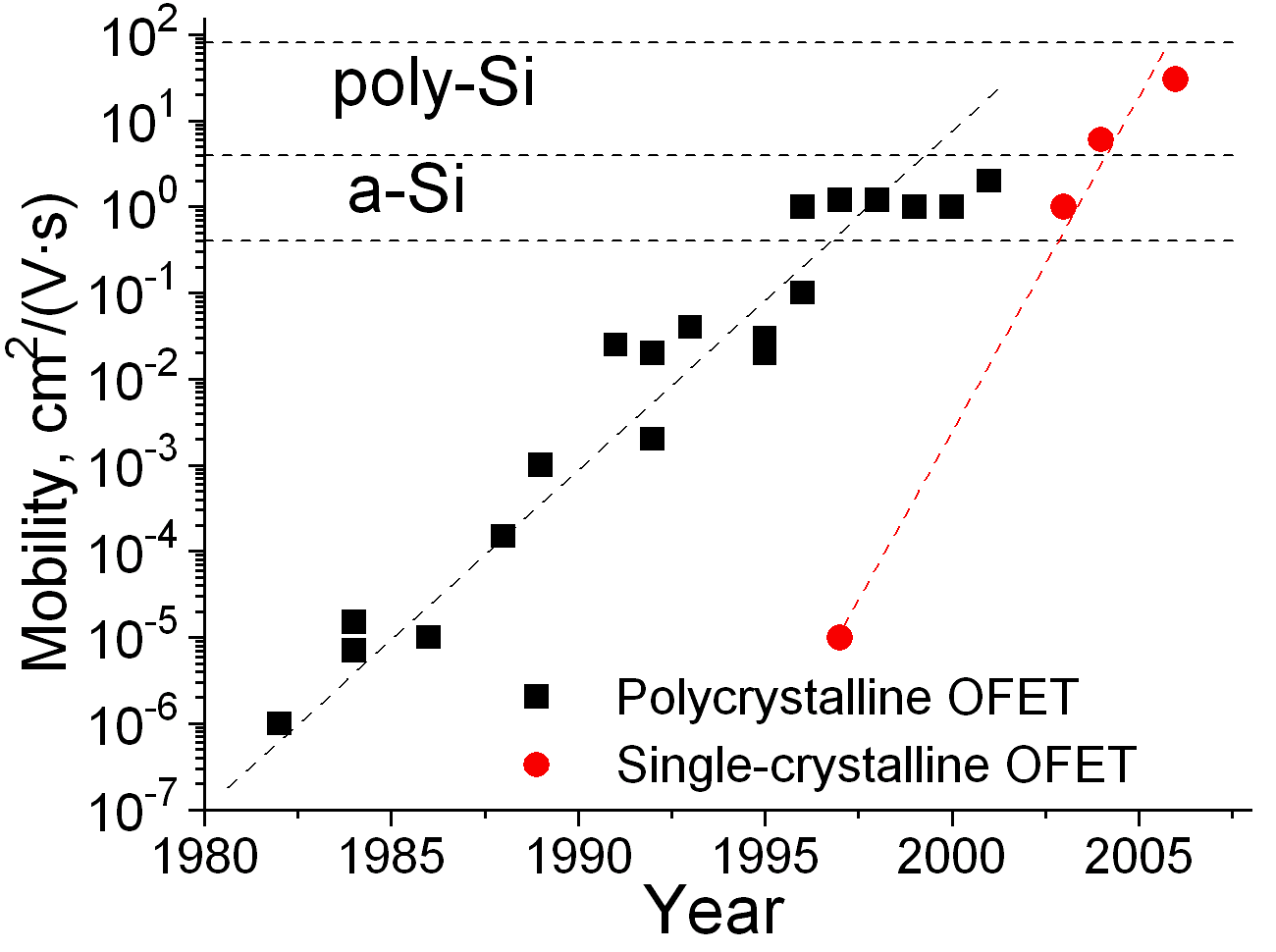
An organic field-effect transistor (OFET) includes an organic semiconductor in its channel. Organic alternatives to amorphous silicon as the active semiconductor in thin-film transistor (TFT) have been the focus of intensive effort in academic and industrial laboratories. OFETs can be prepared either by vacuum evaporation of small molecules, by solution-casting of polymers or small molecules, or by mechanical transfer of a peeled single-crystalline organic layer onto a substrate. These devices have been developed to realize low-cost, large-area electronic products and/or biodegradable electronics. |
|
|
|
(a) OFET-based Flexible Display |
(b) Evolution of Carrier Mobility in OFETs |
|
|
|
|
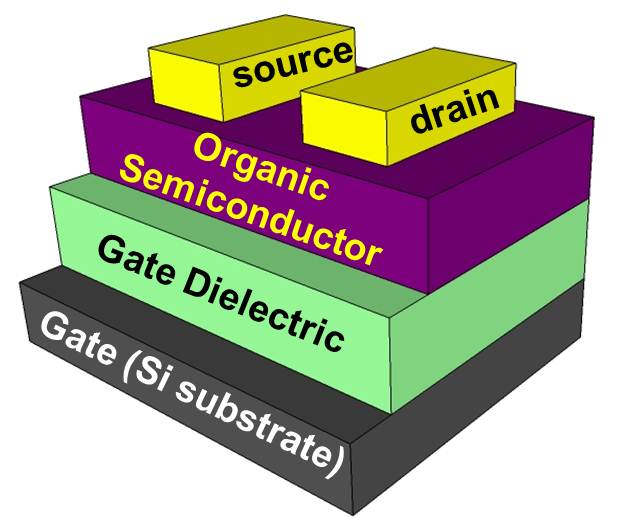
| OFETs have been fabricated with various device geometries. The most commonly used device geometry is bottom gate with top drain- and source electrodes, because this geometry is similar to the TFT using thermally grown Si/SiO2 oxide as gate dielectric. Organic polymers, such as poly(methyl-methacrylate) (PMMA), can be used as dielectric, too. | |
(a) Top Contact Geometry |
(b) Device Characteristics |
 |
|
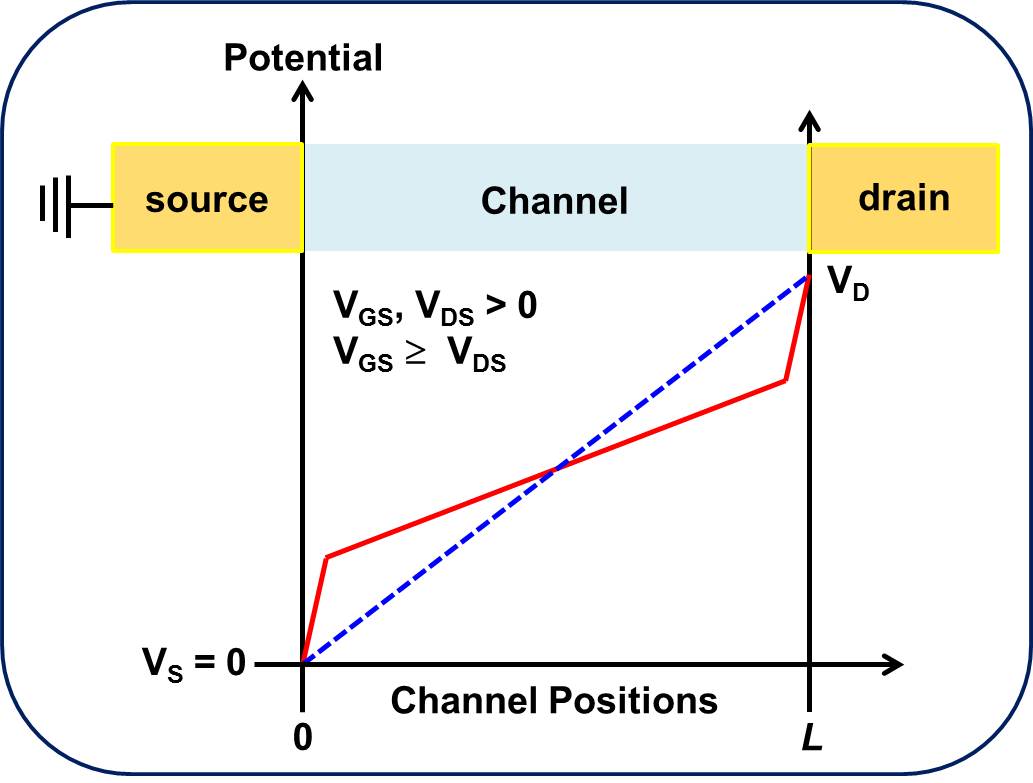
Contact resistances at metal/semiconductor interfaces can limit the performance of OFETs. Optimal devices should display a linear dependence of the channel potential profile and negligible voltage drops at the electrodes. These conditions allow one to accurately determine charge carrier mobilities from device characteristics and lead to low turn-on threshold voltages. |
|
(a) Hypothetical Channel Potential Profile |
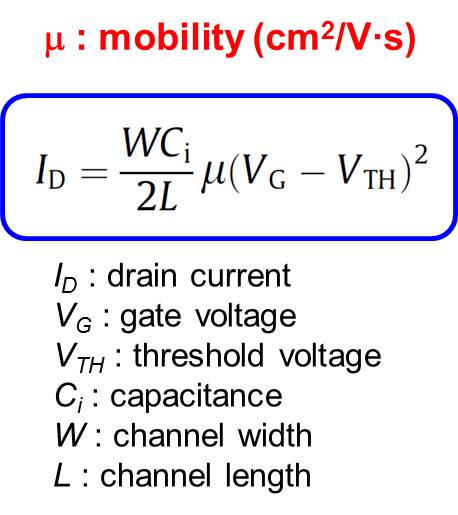
(b) Mobility Equation |
 |
 |
| Reference | |
1. Yan, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Newman, C.; Quinn, J. R.; Dotz, F.; Kastler, M. and Facchetti, A. Nature 2009, 457, 679.
2. Meijer, E. J.; de Leeuw, D. M.; Setayesh, S.; van Veenendaal, E.; Huisman, B. -H.; Blom, P. W. M.; Hummelen,
J. C.; Scherf, U.; and Klapwijk, T. M. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 678.
3. Briseno, A. L.; Mannsfeld, S. C. B.; Ling, M. M.; Liu, S.; Tseng, R. J.; Reese, C.; Roberts, M. E.; Yang, Y.; Wudl, F.;
and Bao, Z. Nature 2006, 444, 913.
4. Cho, S.; Seo, J. H.; Lee, K.; and Heeger, A. J. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 1459.
5. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Organic_field-effect_transistor |
|