| 03 |
|
 |
 |
| Organic light-emitting field-effect transistors (OLETs) are an emerging class of optoelectronic devices that combine the electrical switching functionality of a field-effect transistor (FET) with the capability of light generation typical of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). Due to this unique combination of properties, OLETs have potential applications in the fabrication of simplified pixels for flat panel displays, optical communication devices, and electrically driven organic lasers. |
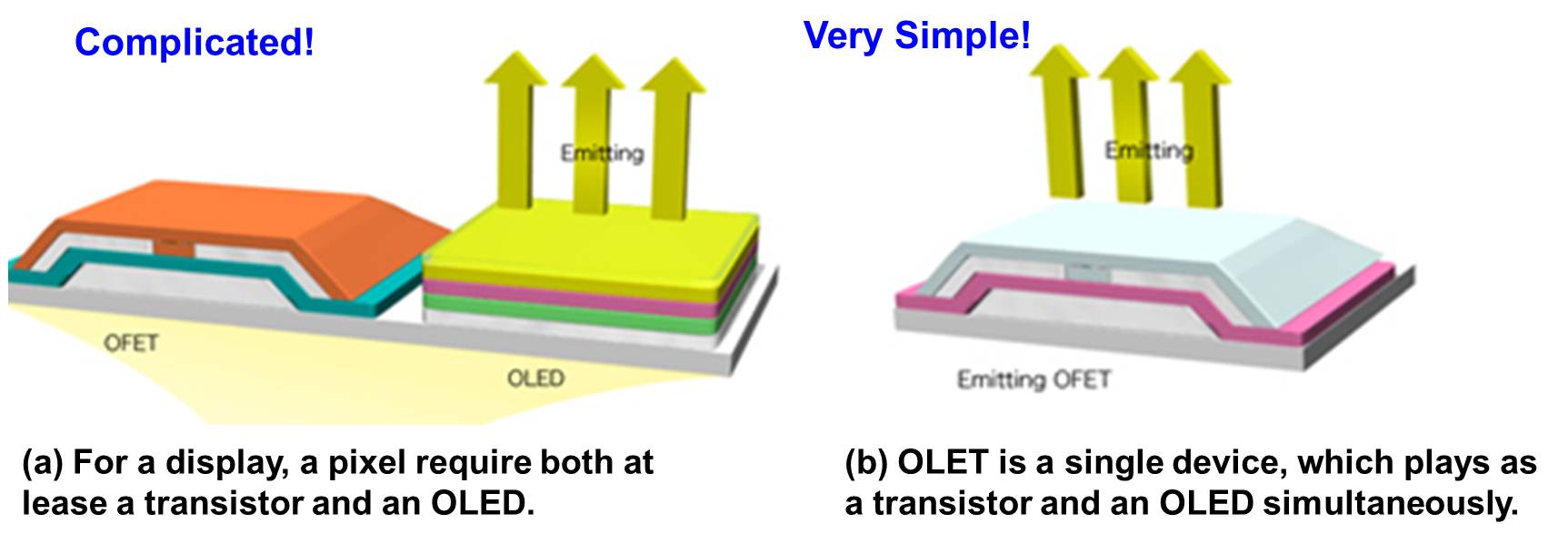 |
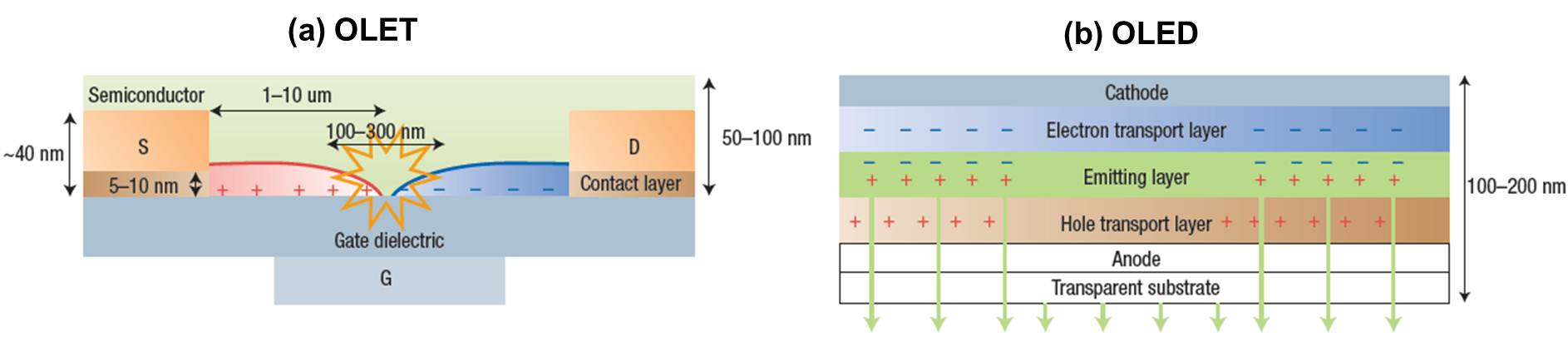
| Injection and transport of both electrons and holes are important requirements for generating electroluminescence in OLETs. Efficient injection of both carriers has been accomplished by using electrodes made from low and high work function WF metals. This choice of metals arises from the contact properties at the organic semiconductor/ metal interfaces, which limit carrier injection. Low WF metals such as Ca, and Mg can be used for facilitating electron injection. However, the complexity of evaporating two different electrodes provides a barrier for widespread implementation of these devices. |
 |
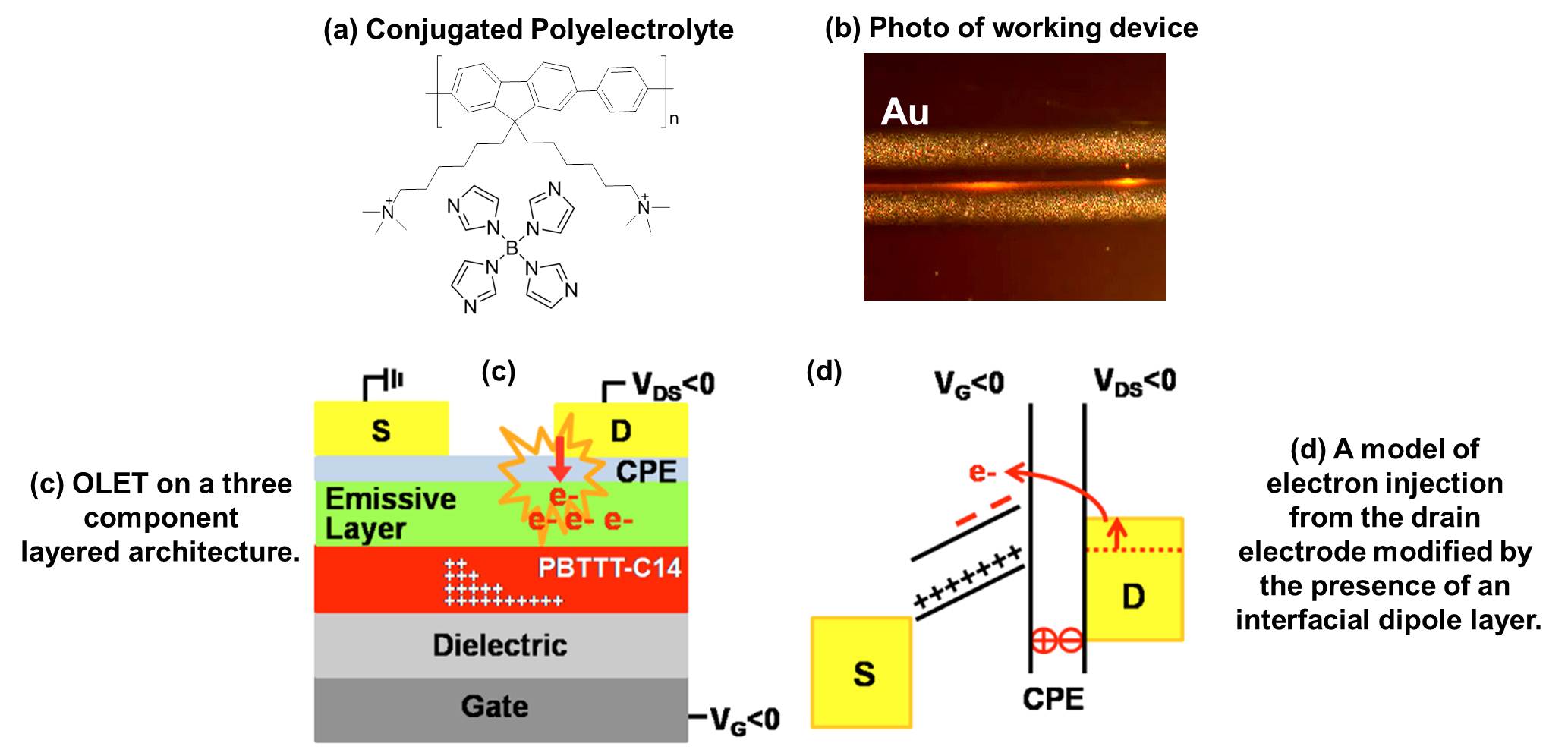
| Seo, et al. disclose a new strategy for simplifying the fabrication of OLET devices with excellent performance by using ionic polymers (conjugated polyelectrolyte, CPE) that effectively modulate charge injection, provided that the thickness is sufficiently thin to avoid possible field redistribution effects. They propose that the thin CPE layers introduce ordered dipoles at the metal/organic semiconductor interface that modify the energy levels and facilitate electron injection. Furthermore, the use of high WF metals for electron and hole injection opens the opportunity of designing OLETs that are less sensitive to environmental degradation. |
 |
| Reference |
1. Muccini, M.Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 605. 2. Sirringhaus, H.; Tessler, N. and Friend, R. H. Science 1998, 280, 1741. 3. Hepp, A.; Heil, H.; Weise,W.; Ahles, M.; Schmechel, R. and von Seggern, H. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 157406. 4. Zaumseil, J.; Friend, R. H. and Sirringhaus, H. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 69. 5. Namdas, E. B.; Tong, M.; Ledochowitsch, P.; Mednick, S. R.; Yuen, J. D.; Moses, D. and Heeger, A. J.Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 799. 6. Seo, J. H.; Namdas, E. B.; Gutacker, A.; Heeger, A. J. and Bazan, G. C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 043303. |



